AI Features in Web Automation
Learn how to use the advanced LLM-powered BELLTRIX features such as element finding by prompt, assertions, self-healing, and smart failure analysis.
Overview
BELLATRIX introduces four advanced AI-powered features for web automation using LLMs:
- Element Finding by Prompt: Locate elements using natural language instructions.
- AssertByPrompt / ValidateByPrompt: Perform assertions and validations using descriptive instructions.
- Native Self-Healing via LLM: Automatic healing of broken tests when the UI changes.
- Smart AI Analysis: Automated root cause analysis, evidence comparison, and failure diagnostics with BDD logging and page snapshots.
These capabilities drastically reduce test maintenance, increase test reliability, and enable true prompt-driven automation for any web application.
Element Finding by Prompt
BELLATRIX allows you to locate web elements directly by describing them in natural language. This enables dynamic and resilient tests, without brittle hardcoded locators.
Example Usage:
// Find by prompt – human-style instruction:
var addToCart = driver.FindElementByPrompt("find Add to cart anchor under 'Falcon 9' item");
addToCart.Click();
// Fallback to locator cache and self-healing
var checkbox = driver.FindElementByPrompt("find out of stock checkbox label under in stock, two elements are returned return the second one");
checkbox.Click();
How it works:
- The framework queries the vector database for known PageObject summaries and tries to map your prompt to a known locator.
- If no known locator is found, or if it fails, the system generates a new XPath using LLM, based on the current DOM summary.
- A cache mechanism stores successful prompt-locator pairs for faster and more robust future runs.
Prompt-driven indexing of Page Objects
If you enable shouldIndexPageObjects in the settings, all POMs are indexed in Qdrant for RAG-based mapping. This increases accuracy and speeds up element resolution.
"largeLanguageModelsSettings": {
//...
"shouldIndexPageObjects": true,
"pageObjectFilesPath": "40. Prompts Support\\Pages"
}
To trigger indexing, call:
WebDriverAiExtensions.IndexAllPageObjects();
You should re-run indexing if you change or add new PageObjects.
AssertByPrompt and ValidateByPrompt
Write human-readable assertions or validations describing expected UI state, using the page’s semantic summary.
Example Usage:
// Using NUnit extension:
driver.AssertByPrompt("the 'Out Of Stock' checkbox is checked");
// Using Bellatrix ValidateByPrompt (fluent style):
ValidateByPrompt("validate that view cart button is visible");
ValidateByPrompt("validate that the total is 54 euro and the vat is 9 euro and -5 coupon applied and exactly 1 item added");
Output:
✅ AI Validate passed: validate that view cart button is visible
✅ AI Validate passed: validate that the total is 54 euro and the vat is 9 euro and -5 coupon applied and exactly 1 item added
How it works:
- BELLATRIX generates a prompt containing the full page summary in JSON and your natural language instruction.
- The LLM outputs “PASS” or “FAIL: [explanation]” for every validation or assertion.
- Failures are reported in your test output with reasoning.
Native Self-Healing via LLM
When a locator fails (due to UI or DOM changes), BELLATRIX automatically:
- Compares the last known working page snapshot with the current one.
- Uses the LLM to generate a new XPath from the detected DOM differences.
- Retries the action with the healed locator (the fallback is not saved permanently, only used for the current run).
- Logs the attempted healing process and result.
Trigger conditions:
enableSelfHealingis set totrueinlargeLanguageModelsSettings.- A locator throws due to element not found or changed attributes/structure.
Typical scenarios:
- IDs or attributes are renamed (e.g.,
emailUpdated→email). - Elements are removed, moved, or have missing labels.
- Buttons/texts are changed (e.g., “Proceed to checkout” → “Checkout”).
Example test trigger:
See test: FillCheckoutFormAndSubmit_SelfHealingEnabled in AutoHealingTests.cs.
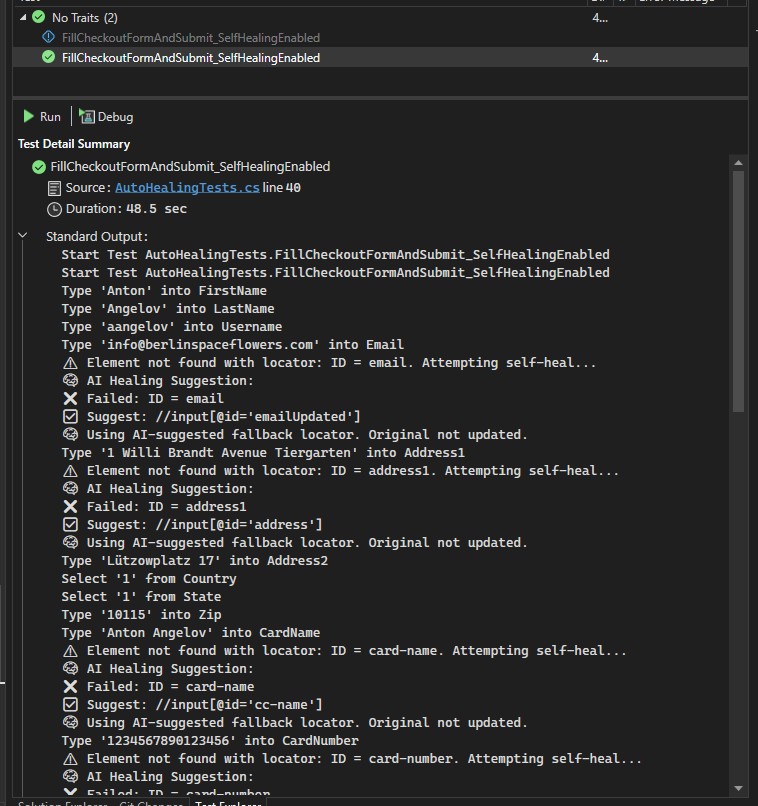
Smart AI Analysis via LLM
On every failure (or optionally every run), BELLATRIX performs a comprehensive AI-driven analysis:
- BDD-style logging: Every test action and assertion is logged in detail.
- Page snapshots: Both successful and failing DOMs are stored and compared.
- Screenshot support: Full-page screenshots on failures.
- Root cause classification: The AI attempts to determine if the problem is a test bug, application bug, or environment issue.
- Detailed recommendations: Step-by-step actions for resolving detected issues.
- Stack trace and visual context are included for debugging.
What Smart AI Analysis Provides:
- Shows you the difference between previous passing and current failing DOM.
- Explains which element or locator failed, why, and what changed.
- Suggests both test and application fixes.
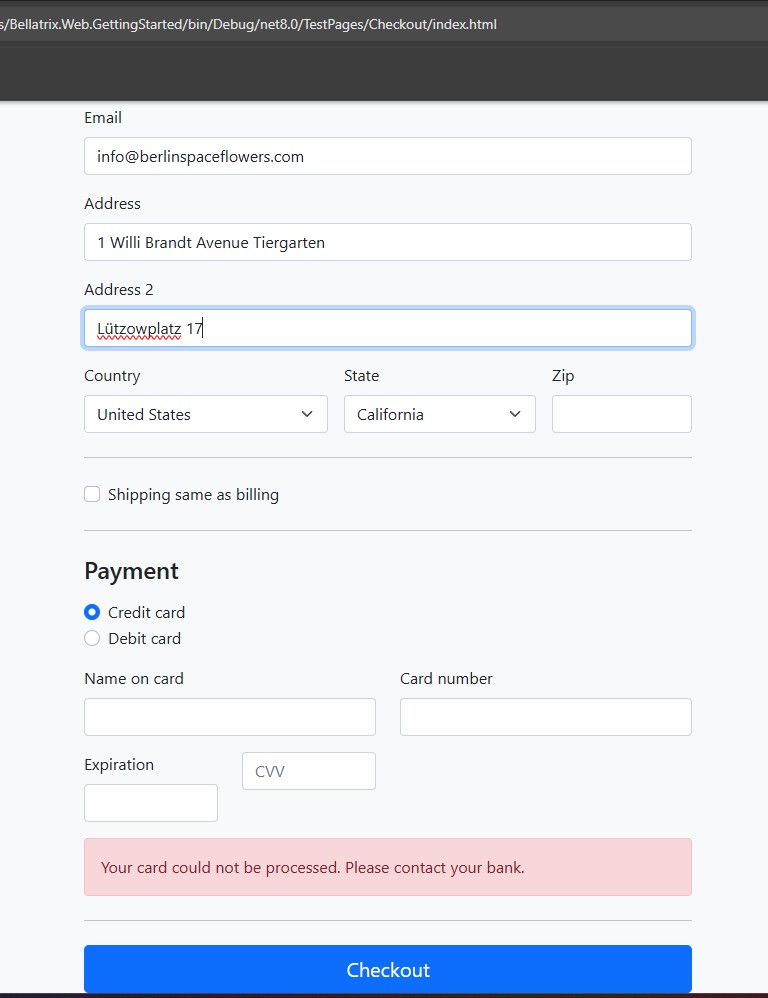
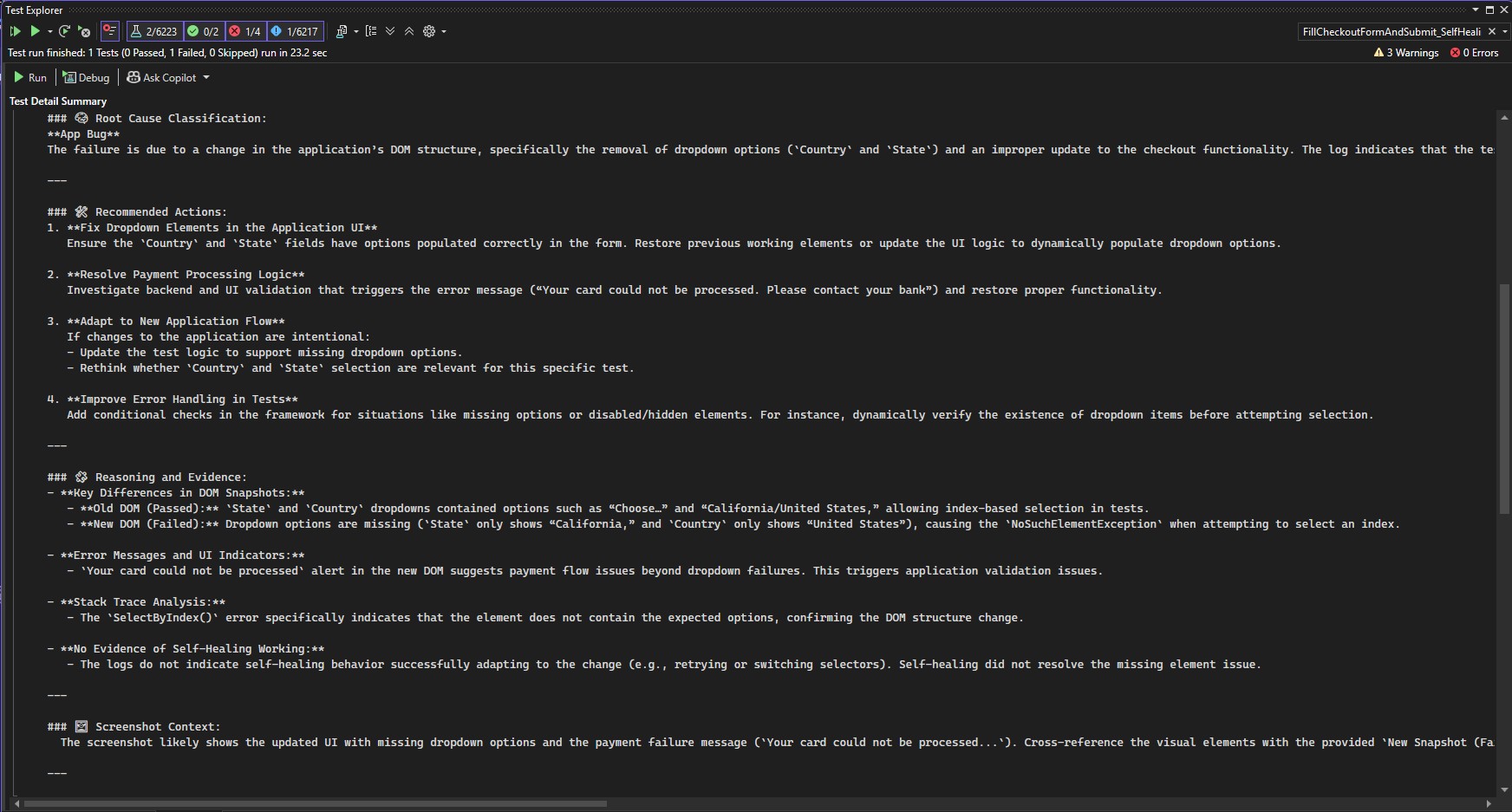
Example output:
🧠 AI-Driven Root Cause Summary:
---
### 🧠 Root Cause Classification:
**App Bug**
The failure is due to a change in the application’s DOM structure...
---
### 🛠 Recommended Actions:
1. **Fix Dropdown Elements in the Application UI**
2. **Resolve Payment Processing Logic**
3. **Adapt to New Application Flow**
4. **Improve Error Handling in Tests**
---
### 🧩 Reasoning and Evidence:
- **Key Differences in DOM Snapshots:**
- **Error Messages and UI Indicators:**
- **Stack Trace Analysis:**
- **No Evidence of Self-Healing Working:**
---
### 🖼️ Screenshot Context:
The screenshot likely shows the updated UI with missing dropdown options and the payment failure message.
Configuration and Settings
All main AI features are controlled in testFrameworkSettings.Debug.json under the section largeLanguageModelsSettings.
Sample settings:
"largeLanguageModelsSettings": {
"modelSettings": [
{
"endpoint": "env_AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT",
"key": "env_AZURE_OPENAI_KEY",
"deployment": "gpt-4o"
},
{
"serviceId": "openai-embed",
"endpoint": "env_AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDINGS_ENDPOINT",
"key": "env_AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDINGS_KEY",
"embeddingDeployment": "text-embedding-ada-002"
}
],
"qdrantMemoryDbEndpoint": "http://localhost:6333",
"localCacheConnectionString": "env_LocalCacheConnectionString",
"localCacheProjectName": "web_getting_started",
"shouldIndexPageObjects": false,
"pageObjectFilesPath": "40. Prompts Support\Pages",
"memoryIndex": "PageObjects",
"resetIndexEverytime": false,
"locatorRetryAttempts": 5,
"validationsTimeout": 15,
"sleepInterval": 1,
"enableSelfHealing": true,
"enableSmartFailureAnalysis": true
}
Where to set up:
- The configuration file is found in Bellatrix.LLM project’s root folder.
- If you run in Docker, set your model endpoints and keys as environmental variables.
Initial Docker Compose for Local Qdrant and PostgreSQL cache:
docker-compose -f docker-compose.local_cache_postgres.yml up -d
- You can find the compose file in the root folder of the Bellatrix.LLM project.
- In the cloud, deploy your own Qdrant instance and set the connection string and endpoint in your config/environment variables.
- Environmental variables required:
AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINTAZURE_OPENAI_KEYAZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDINGS_ENDPOINTAZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDINGS_KEYLocalCacheConnectionString
DB Caching Mechanism:
- Successfully resolved locators for prompts are stored locally in the cache.
- This allows re-use and “self-healing” between runs – no repeated AI calls for the same instruction if the locator didn’t change.
- The cache is resettable per project via
localCacheProjectName.
Troubleshooting & Examples
- If a test heals itself, you will see log entries such as:
⚠️ RAG-located element not present. Trying cached selectors...🧠 Caching new selector for 'find 'Saturn V' quantity number input': //input[@id='quantity_6836c067a6729']✅ Using cached selector.
- If healing fails, smart AI analysis explains exactly why, and what to do next.
- You can use the provided standard output and AI analysis blocks as templates for what to expect.
Shadow DOM Support
BELLATRIX fully supports Shadow DOM automation, including:
- Locating elements in nested shadow roots by prompt, XPath, or CSS.
- AI-based smart failure analysis and healing inside Shadow DOM elements.
- The prompt-driven locator logic works seamlessly inside and outside shadow trees.
How it works:
- Shadow DOM roots and element structure are parsed and included in the JSON DOM summary.
- You can use
FindElementByPromptto locate any element, even in deeply nested Shadow DOM scenarios.
Refer to shadow-dom.md for deep technical details.